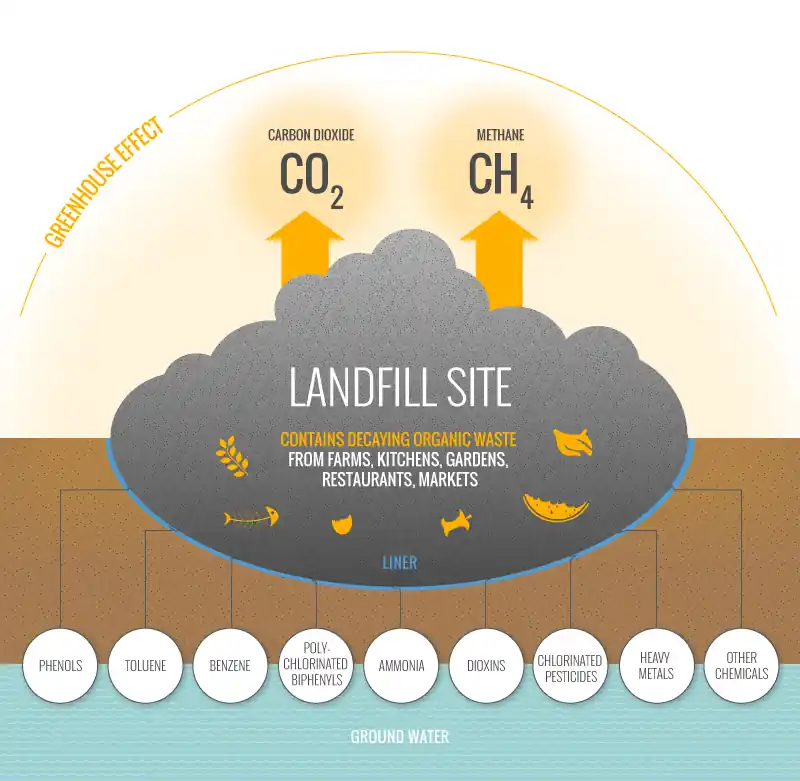
So, which gas is produced from landfill waste? Landfill waste is known for creating harmful gases. The main gases are methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Knowing which gas comes from landfills is key for protecting our environment and finding new energy sources.
The gases from landfills harm our climate and health. This makes it important to manage these gases well.
Key Takeaways
- Landfill waste mainly produces methane and carbon dioxide.
- Understanding these gases helps address their environmental impact.
- Methane from landfills is a potent greenhouse gas.
- Landfill gas management is vital for reducing health risks.
- Good management can turn landfill gas into energy.
Understanding Landfill Gas Composition
Landfill gas is a mix of gases from organic material in landfills. Knowing its makeup is key to understanding its effects.
Main Components
The main components of landfill gas are methane and carbon dioxide. Methane makes up 45-60% and carbon dioxide 40-60%. Nitrogen and oxygen are also present, but in smaller amounts.
Here's a detailed overview of the primary gases found in landfill gas:
| Gas | Proportion (%) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Methane | 45-60 | Major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions |
| Carbon Dioxide | 40-60 | Greenhouse gas contributing to climate change |
| Nitrogen | 2-5 | Typically inert but influences gas behavior |
| Oxygen | 0-1 | Critical for microbial activity |
Trace Gases
Landfill gas also has trace gases. These gases, like VOCs, hydrogen sulfides, and ammonia, are present in small amounts. But they can have big effects on the environment and health.
Here is a look at some of the common trace gases found in landfills:
| Trace Gas | Possible Effects |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Sulfides | Odor problems, respiratory issues |
| Ammonia | Can cause irritation to eyes, skin, and respiratory system |
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | Impact air quality, possible health risks |
Knowing the landfill gas composition helps manage emissions. It's key to protecting the environment and human health. By watching the main components of landfill gas and trace elements, we can improve waste management and methane reduction.
How Landfill Gas is Produced
The process of making landfill gas is complex. It involves three main parts: bacterial decomposition, volatilization, and chemical reactions.
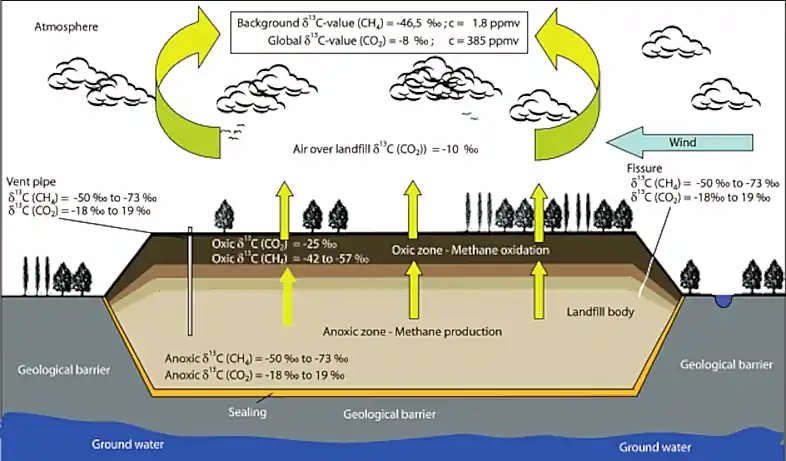
“Schematic Sketch of Landfill Gas …” from www.researchgate.net and used with no modifications.
Bacterial Decomposition
Bacterial decomposition is key in making landfill gas. Bacteria break down organic waste. They make biogas, mostly methane and carbon dioxide, without oxygen.
Volatilization
Volatilization is also important. It turns solid or liquid waste into gas. This gas adds to the landfill gas. High temperatures help this process.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions also play a big role. They happen between different waste materials. For example, they can make gases like hydrogen sulfide. These reactions, along with bacterial decomposition and volatilization, make landfill gas.
The Stages of Bacterial Decomposition in Landfills
The process of bacterial decomposition in landfills has four main stages. Each stage is important for turning organic waste into gas. This gas is mostly methane and carbon dioxide. Knowing these stages helps in managing landfill gas better.
Phase I: Initial Breakdown
In the first stage, complex organic materials start to break down. Aerobic bacteria do this work. They use oxygen and make carbon dioxide.
Phase II: Acid Formation
The second stage is about acid formation. Here, anaerobic bacteria make volatile fatty acids and gases. These include carbon dioxide and hydrogen. This makes the environment more acidic, helping break down waste further.
Phase III: Methanogenesis
The third stage is all about methane production. Methanogenic bacteria turn acids into methane and carbon dioxide. This is when methane starts to form in big amounts.
Phase IV: Stabilization
The final stage is stabilization. Here, gas production becomes steady. This stage is key for keeping methane and carbon dioxide levels even.

Which Gas is Produced from Landfill Waste: The Gas It Produces
Understanding which gas is produced from landfill waste shows us a lot about the environment and energy. The main gas from landfills is methane. It's a strong greenhouse gas that affects our climate.
Methane comes from the breakdown of organic materials in landfills. Bacteria break it down in several steps. This leads to methane, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Knowing this helps us see the chance to use methane as energy.
It's important to manage which gas is produced from landfill waste. We can capture and use methane to cut down on greenhouse gases. This helps us meet climate goals and shows how waste can be turned into energy.
Factors Affecting Landfill Gas Production
Many things affect how much gas a landfill makes. What kind of waste is there matters a lot. Stuff like food scraps and yard trimmings breaks down fast and makes more gas.
Environmental factors also play a big part. For example, how hot or cold it is can change how fast waste breaks down. When it's warmer, waste breaks down faster, making more gas. But when it's colder, it breaks down slower.
How wet the landfill is is also important. If it's just right, waste breaks down well and makes more gas. But too much water can stop gas production for a while.
The amount of oxygen in the landfill is key too. Without oxygen, special bacteria break down waste and make methane gas. This is why it's important to keep oxygen out of landfills to make more methane.
How long waste has been in the landfill also matters. New waste makes gas fast because it breaks down quickly. But as waste gets older, it makes gas slower. Yet, some waste can keep making gas for a long time.
Knowing how all these things affect gas production is very important. It helps waste managers and gas capture teams do their jobs better. By controlling these factors, they can make more gas and reduce harm to the environment.
Movement and Migration of Landfill Gas
The movement of landfill gas is complex. It's influenced by many factors. Knowing how gas moves helps us manage its effects on the environment and health.
Gas moves up and sideways. These movements are affected by several things.
Upward Movement
Landfill gas goes up through the soil. This is because of pressure differences between the landfill and the surface. The pressure in the landfill pushes gases up to the surface.
Soil's ability to let gas pass through is key. It helps or blocks gas movement.
“Landfill Gas Monitoring Systems …” from www.geoengineer.org and used with no modifications.
Horizontal Movement
If gas can't go up, it moves sideways. This is when gas hits dense materials like clay. It then spreads out into nearby areas.
This can harm nearby buildings and nature. It's important to watch and control this movement.
Factors Influencing Migration
Many things affect how landfill gas moves. These include diffusion, pressure changes, and soil's ability to let gas pass.
Diffusion spreads gas molecules. Pressure pushes gas to move. Soil's permeability decides how gas can pass through.
Environmental and Health Impacts of Landfill Gas Emissions
Landfill gas emissions are harmful to the environment and our health. Methane, a strong greenhouse gas, is a big problem. It makes global warming worse.
Climate Change Implications
Methane's effect on climate change is huge. It traps heat more than carbon dioxide. This speeds up climate change.
The environment suffers from rising temperatures and extreme weather. Ecosystems also get disrupted.
Health Risks
Landfill gas emissions also harm our health. People living near landfills face many health problems. These include breathing issues and long-term effects from toxic gases.
Technological Solutions for Managing Landfill Gas
Big steps have been made in using landfill gas in a good way. This helps reduce the bad effects of landfill gases. We can now make the environment better and use the gases for good things.
Gas Collection Systems
Gas collection systems are key in handling landfill gases. They use wells to grab the gas from the landfill. The gas can then be treated or used to keep the environment safe.
Many places use these systems to make their landfills better.
Flaring and Combustion
Landfill gas flaring is also common. It burns the gas to make it less harmful. This way, pollution is kept down and safety is increased.
Technologies for burning gas are getting better. They help landfills be less bad for the environment.
Energy Recovery Programs
Energy recovery programs turn landfill gas into something useful. They make methane into energy. This energy can power homes or businesses.
These programs help communities use clean energy. They fit well with plans to make energy more sustainable.
Renewable Energy from Landfill Gas
Landfill gas (LFG) is a big source of renewable energy. We can turn it into useful energy. This helps the environment and supports sustainability.

“Turning COP26 methane promises into …” from blogs.edf.org and used with no modifications.
Electricity Production
Electricity production is a key use of landfill gas. We capture methane and turn it into electricity. This cuts down on greenhouse gas emissions and adds clean energy to the grid.
Direct Use Applications
Direct use is another good way to use landfill gas. It can power nearby industrial plants and heating systems. This method cuts down on carbon emissions and saves money on energy.
Alternate Fuels
Turning landfill gas into alternative fuels is a smart move. We can make it into natural gas or CNG. This reduces our need for fossil fuels and offers cleaner energy.
Case Studies of Successful Landfill Gas Utilization Projects
Many landfill gas projects have shown great success over the years. They prove the huge value of turning landfill gas into energy. These projects use new ideas and bring real benefits to the environment and local people.
The Fresh Kills Landfill in Staten Island, New York, is a great example. It turned a big problem into a solution, making enough energy to power thousands of homes. New gas collection and energy tech were key to its success.
In North Carolina, the Brunswick Landfill is another success story. It uses the latest tech to make electricity and heat, cutting down on harmful emissions. This project is a guide for others wanting to fight climate change and grow their economy.
The Puente Hills Landfill in California also shows the power of landfill gas. It uses different ways to make energy, making the most of every resource. This approach helps the environment and supports sustainability.
“A well-executed landfill gas project not only curtails methane emissions but also contributes to the local economy by creating jobs and providing a steady stream of renewable energy,” noted Mary Ann Smith, Director of Renewable Energy Programs.
These examples show how landfill gas can be turned into something valuable. They show the big change possible in waste management. These projects offer a path for a greener future.
Current Regulations and Policies Regarding Landfill Gas
Managing landfill gas is key to lessening environmental harm. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has strict landfill gas regulations. These rules help manage methane emissions well.
EPA Regulations
The EPA is a big player in landfill gas rules. EPA policies on methane emissions make landfills use gas collection systems. This helps cut down on harmful gases. Following these rules is important for the planet and people's safety.
State-Level Policies
State regulations for landfill gas differ in the U.S. Some states have stricter rules than the federal government. They ask for advanced tech for managing landfill gas. These rules help tackle local environmental issues and support green waste management.
Incentives and Support Programs
Many groups offer money and help to follow landfill gas rules. These programs give funding and advice to landfills. They help landfills use the best methods and new tech for gas management.
| Regulatory Authority | Key Focus Area | Examples of Policies |
|---|---|---|
| EPA | Methane Emission Control | Require gas collection systems, monitoring |
| California | Enhanced Emission Standards | Stricter than federal regulations |
| New York | Renewable Energy Utilization | Incentives for landfill gas-to-energy projects |
Which Gas is Produced from Landfill Waste – An End Note
Understanding and managing landfill gas is key for the environment and our health. Landfill gas is mostly methane and carbon dioxide, made by bacteria breaking down waste. Good management means knowing the mix of gases and using new tech to capture and use the gas well.
Less landfill gas means better air and health. New tech, like gas collection systems, helps. It turns a problem into a useful resource. This shows why we need to keep improving how we handle landfill gas.
Rules and state policies help manage landfill gas well. Following EPA guidelines and using incentives can cut down on carbon and use gas energy. Working together, we can make a greener, healthier world.
Which Gas is Produced from Landfill Waste? FAQs
Which gas is mainly produced from landfill waste?
What is the composition of landfill gas?
How is landfill gas produced?
What are the stages of bacterial decomposition in landfills?
What factors influence landfill gas production?
How does landfill gas move and migrate?
What are the environmental and health impacts of landfill gas emissions?
What technologies exist for managing landfill gas?
How can landfill gas be utilized as a renewable energy source?
Are there any successful landfill gas utilization projects in the United States?
What are the current regulations and policies regarding landfill gas?
The Future of Sustainable Bio-based Materials and Products
Bio-based materials are products and materials made from renewable biological resources like plants, animals, and microorganisms. They are a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil-fuel-based products, offering advantages such as a smaller carbon footprint and reduced reliance on finite resources. Common examples include timber, hemp, and bio-based plastics like polylactic acid (PLA), and they are used […]
A Success Story: LFG-to-Energy Conversion Units Transforming Landfill Gas in California
California's landfill gas-to-energy conversion units are redefining waste management by transforming captured methane into electricity, renewable natural gas for vehicles, and liquefied natural gas. These advancements mark a significant step towards sustainability, reducing carbon footprints and turning waste into a valuable, clean energy resource…
Best Low Carbon Farming Practices & Techniques
Farmers are turning to low carbon techniques like no-till farming and precision agriculture to combat climate change. These practices not only reduce emissions but also improve soil health and farm profitability, offering a resilient future for agriculture as weather patterns grow increasingly unpredictable…
Integration of Biogas Systems into the Energy System
Key Takeaways Biogas systems can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels by providing a renewable energy source. They play a crucial role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change. Biogas systems offer scalable energy solutions tailored to local needs, particularly in rural areas. Integrating biogas into existing energy grids can enhance grid stability […]